How Golden Link® Microbials Work
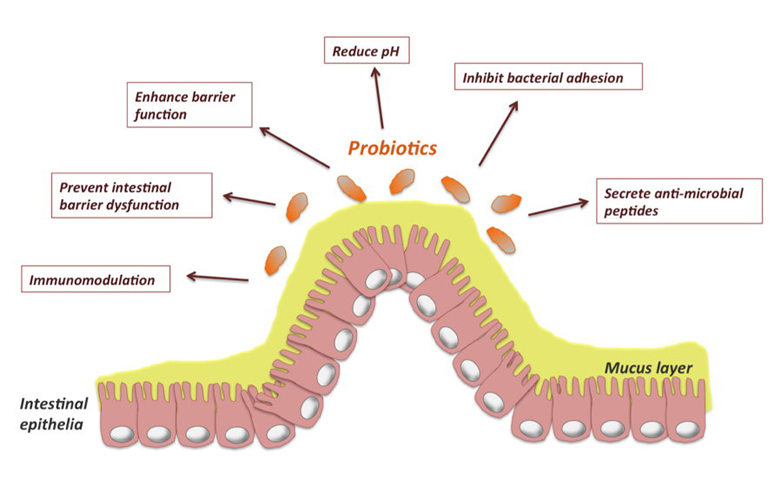
Probiotic is derived from the Greek word “pro” meaning “for” and “biosis” meaning “life”. Therefore, “pro-biotic” is and means “for-life”. Thus, probiotic supplements can be defined as helpful bacteria strains capable of doing the following:
- Colonizing and surviving in the gut which will have a beneficial effect on their host by suppressing the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Interacting and stimulating the immune system.
- Breaking down and helping the digestion of cellulose, starches, and proteins by enzyme production.
Probiotics work to promote a healthy immune system in the small and large intestine of the equine, bovine and companion animals.
The breakdown of food stuff occurs in the rumen and small intestine of the bovine, the hind gut and small intestine of the equine and the small intestine of the companion animal.
So, how do microbes, in the Direct Fed Microbials (DFM), work to stimulate immunity in the bovine, equine, and companion animal?
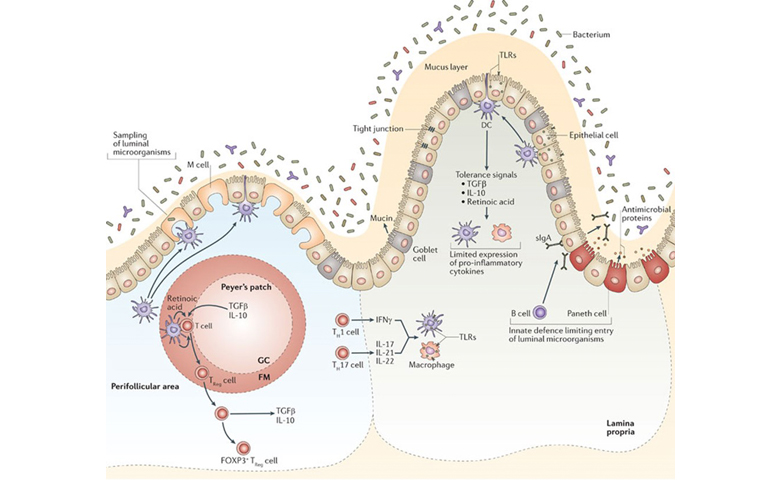
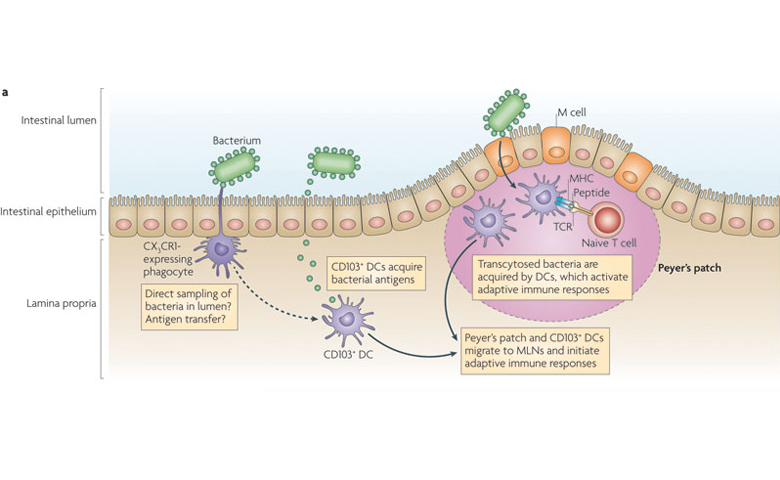
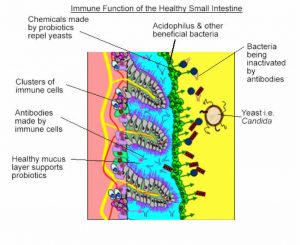 There is a profound link between the gut of all animals, humans included, and the immune system.
There is a profound link between the gut of all animals, humans included, and the immune system.
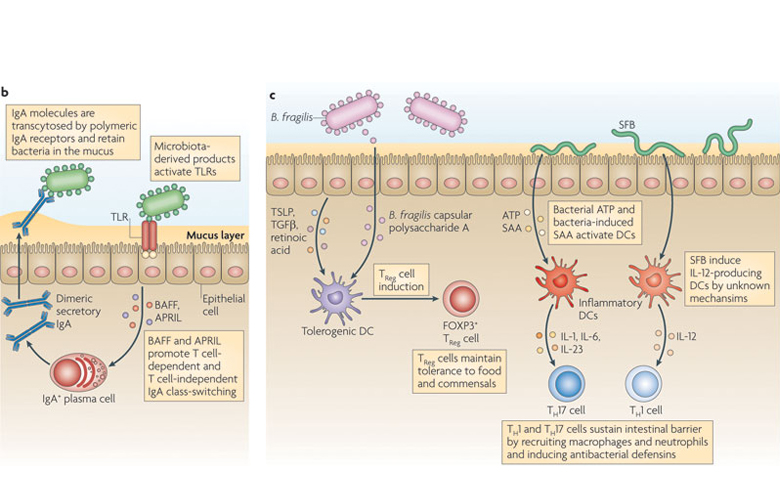
We typically think of the intestinal tract as a digestive organ but it also has a very important role in the immune system of all animals. This is because 70-80% of the immune system of animals is located in the gut associated lymph node tissue (G.A.L.T.). Because the immune system is located in the G.A.L.T., what occurs here has a profound influence of an animal’s entire immunity and this immune system can further be divided into two functions or arms.
- The first part or arm, is related to the production of antibodies and T cells. This is the arm that is most easily identified with and understood.
- The second part or arm, is the less understood arm of the immune system can be labeled the “innate immune system”. This system does not target specific organisms, like bacteria or viruses like the sophisticated arm, but has what is called a “knee jerk” reaction to anything in the blood or tissues perceived as foreign or harmful. This is the arm that is triggered by stress from cortisol and epinephrine and is the part of the immune system that is most waning in stressful conditions. It is here that the probiotic influence is most helpful and recognized.
Probiotics for Digestion
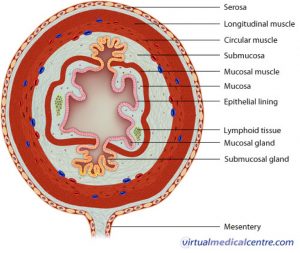
Because very little digestion occurs in the true stomach of the bovine or equine, probiotics do their work in the rumen and hind gut of the bovine and equine respectively. In the companion animal, most digestion occurs in the small intestine and stomach.
Probiotic bacteria have been found to help in the restoration of the ruminal and hind gut eco systems. The restoration in the companion animal occurs mostly in the small intestine. Bacteria in the ruminant and equine helps break down fiber though the production of enzymes. Along with the production of enzymes, break down of the fiber is promoted by the stimulation and growth of beneficial bacteria. In the companion animal, enzymes are also produced by beneficial bacteria in the small intestines.
Yeast
The addition of yeast to a probiotic supplement is for the purpose of their positive stimulatory effect on the bacterial population in the rumen of the bovine and hind gut of the equine. The physiological basis for the enhanced microbial growth has been described in that yeast provides important nutrients or nutritional cofactors that stimulate microbial activities and control O2 levels.
Yeast and yeast culture are not one of the same. Yeast are individual organisms and are live growing individual cellular organisms.
Yeast culture, on the other hand, is a product that is the substrate where the individual yeast organisms propagate or are grown. This substrate where the fermentation process of growing yeast takes place is called yeast culture.
In addition to the live yeast organisms, contained in the culture there is also useful enzymes that are produced in the process of fermentation. It is the addition of this yeast culture, rich in enzymes, that helps digestion in the companion animal.
This combination of the yeast organisms and the substrate or (yeast culture), in addition to its digestive properties, is added to the probiotic supplement to nourish the bacteria once fed to the herbivore animal.
Enzymes
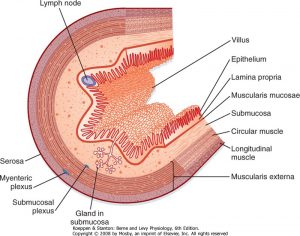
Enzymes are one of the most important factors for digestion in all animals. Enzymes are protein molecules that function to catalyze (speed up) the breakdown of fed products. The enzymes are specific to the breakdown of specific substrates. Since feeds are categorized as carbohydrates, fats and protein, the enzymes that are produced are categorized also by what food group they are active against, alpha amylase- breaks down carbohydrates, protease-helps digest protein into amino acids, cellulase- breaks down the fiber cellulose into available sugars.
Our Enzymes
By adding enzymes to the probiotic mixture, you are essentially aiding the breakdown of the food stuff fed to the animal’s small intestine where much of the absorption begins to takes place. Also, in the rumen of the bovine and the hind gut of the equine, where much cellulose is broken down and utilized.
Viability
Like helpful bacteria (probiotics), yeast and enzymes are sensitive to their environment. Periods of extreme heat, extended storage and moisture will render these products less that satisfactory for their intended use in a product.